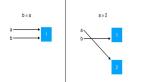
解密Python list 深/淺拷貝原理
1. python list的深/淺拷貝
python 有一種常用數(shù)據(jù)類型:list,使用list時(shí)經(jīng)常需要考慮一件事件,那就是:淺拷貝與深拷貝。
至于什么是深淺拷貝,先從一個(gè)示例代碼來(lái)分析一下:
- import copy
- # list 測(cè)試使用的源數(shù)據(jù)
- lists = [[1, 2, 3], 4, 5, 6]
- def low_copy():
- # list 淺拷貝
- low_list = copy.copy(lists)
- return list(low_list)
- def deep_copy():
- # list 深拷貝
- deep_list = copy.deepcopy(lists)
- return list(deep_list)
- if __name__ == "__main__":
- print("源 list:", lists)
- # 分別獲取 淺拷貝、深拷貝 list對(duì)象
- lists_c = low_copy()
- lists_d = deep_copy()
- print("淺拷貝 list:", lists_c)
- print("深拷貝 list:", lists_c)
- print("========================")
- # 對(duì)源數(shù)據(jù)的 第0下數(shù)據(jù)追加數(shù)值7
- print("對(duì)源list的第0下數(shù)據(jù)追加數(shù)值7,start")
- lists[0].append(7)
- print("對(duì)源list的第0下數(shù)據(jù)追加數(shù)值7,end")
- print("========================")
- # 源數(shù)據(jù)的 第0下數(shù)據(jù)追加數(shù)值7 之后驗(yàn)證,深淺拷貝數(shù)據(jù)的變化
- print("源 list:", lists)
- print("淺拷貝 list:", lists_c)
- print("深拷貝 list:", lists_d)
- # 執(zhí)行結(jié)果
- #
- # 源 list: [[1, 2, 3], 4, 5, 6]
- # 淺拷貝 list: [[1, 2, 3], 4, 5, 6]
- # 深拷貝 list: [[1, 2, 3], 4, 5, 6]
- # ========================
- # 對(duì)源list的第0下數(shù)據(jù)追加數(shù)值7,start
- # 對(duì)源list的第0下數(shù)據(jù)追加數(shù)值7,end
- # ========================
- # 源 list: [[1, 2, 3, 7], 4, 5, 6]
- # 淺拷貝 list: [[1, 2, 3, 7], 4, 5, 6]
- # 深拷貝 list: [[1, 2, 3], 4, 5, 6]
通過(guò)示例代碼可以看出:在對(duì)list進(jìn)行淺拷貝、深拷貝之后,對(duì)源數(shù)據(jù)進(jìn)行修改,則會(huì)直接影響淺拷貝的數(shù)據(jù),深拷貝的數(shù)據(jù)則無(wú)影響。
這說(shuō)明了什么,具體又是怎么實(shí)現(xiàn)的呢?
2. pyhton list 的實(shí)現(xiàn)
首先,要說(shuō)明幾點(diǎn):
- python 底層源碼使用C語(yǔ)言實(shí)現(xiàn)
- 在 python 中一切皆對(duì)象(整數(shù)、字符串,甚至類型、函數(shù)等都是對(duì)象)
python的對(duì)象,大概分為以下幾種:
參考 https://flaggo.github.io/python3-source-code-analysis/objects/object/
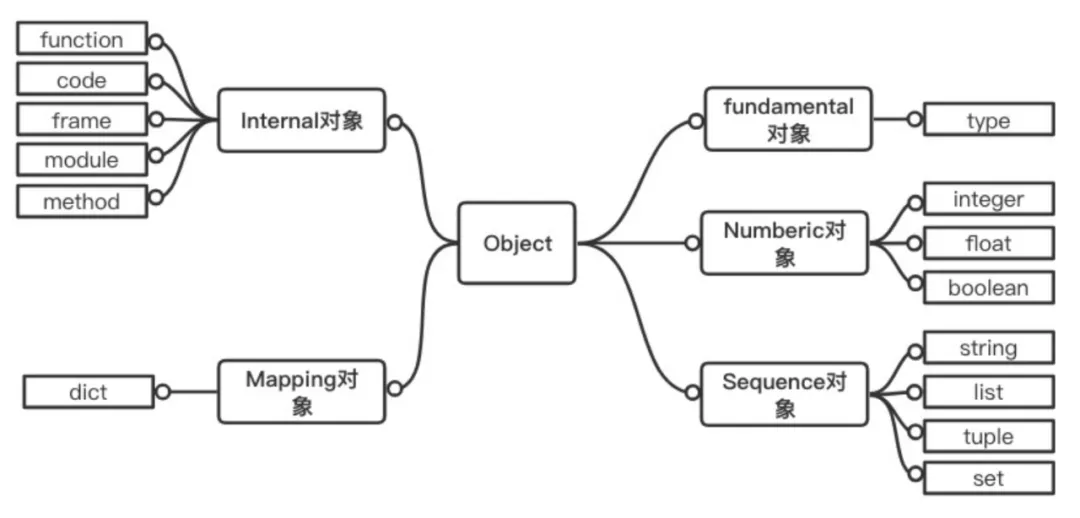
- Fundamental 對(duì)象: 類型對(duì)象
- Numeric 對(duì)象: 數(shù)值對(duì)象
- Sequence 對(duì)象: 容納其他對(duì)象的序列集合對(duì)象
- Mapping 對(duì)象: 類似 C++中的 map 的關(guān)聯(lián)對(duì)象
- Internal 對(duì)象: Python 虛擬機(jī)在運(yùn)行時(shí)內(nèi)部使用的對(duì)象
3. list 對(duì)象
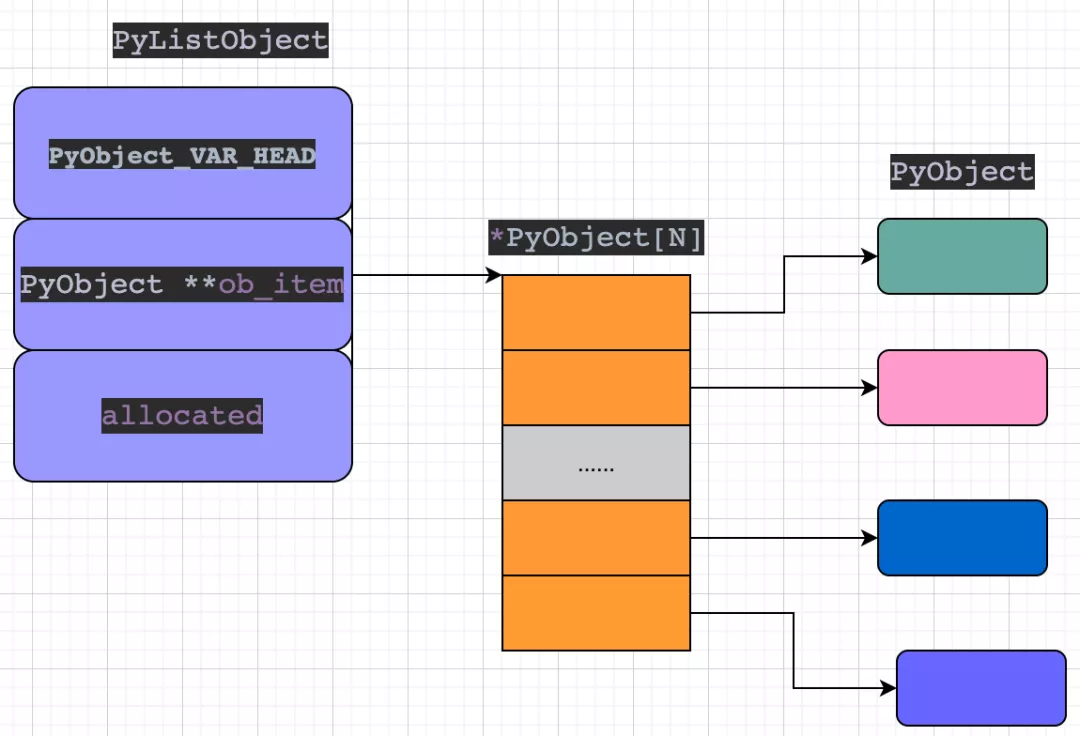
在python的源碼實(shí)現(xiàn)中,list的結(jié)構(gòu)體如下:
- // 源文件:Include/listobject.h
- // listobject.h
- typedefstruct {
- // 對(duì)象的公共頭部
- PyObject_VAR_HEAD
- // 指向 list 元素的指針向量,list[0] 就是 ob_item[0]
- // 可以看到 ob_item 是個(gè)二級(jí)指針
- // 也就是說(shuō) **ob_item 表示它是指向 PyObject類型指針數(shù)組 指針
- // *ob_item 表示它是 PyObject類型指針數(shù)組
- /* Vector of pointers to list elements. list[0] is ob_item[0], etc. */
- PyObject **ob_item;
- /* ob_item contains space for 'allocated' elements. The number
- * currently in use is ob_size.
- * Invariants:
- * 0 <= ob_size <= allocated
- * len(list) == ob_size
- * ob_item == NULL implies ob_size == allocated == 0
- * list.sort() temporarily sets allocated to -1 to detect mutations.
- *
- * Items must normally not be NULL, except during construction when
- * the list is not yet visible outside the function that builds it.
- */
- // list 容納元素的總數(shù)
- Py_ssize_t allocated;
- } PyListObject;
從 list 的結(jié)構(gòu)體可以看出,真正存儲(chǔ)對(duì)象的是 ob_item 字段,該字段是一個(gè)指向 指針數(shù)組 的指針,從而得知 PyListObject 結(jié)構(gòu)體是一個(gè)多級(jí)結(jié)構(gòu)體。
創(chuàng)建list的過(guò)程主要分為兩個(gè)步驟:
- 創(chuàng)建 PyListObject 結(jié)構(gòu)體
- 對(duì) ob_item 指向的指針數(shù)組進(jìn)行初始化操作
- // 源文件位置:Objects/listobject.c
- // 創(chuàng)建一個(gè)新的 list
- PyObject *
- PyList_New(Py_ssize_t size) {
- // 判斷創(chuàng)建 list 時(shí)的 size 是否合法
- if (size < 0) {
- PyErr_BadInternalCall();
- returnNULL;
- }
- struct _Py_list_state *state = get_list_state();
- // 最終創(chuàng)建的 list 對(duì)象指針
- PyListObject *op;
- #ifdef Py_DEBUG
- // PyList_New() must not be called after _PyList_Fini()
- assert(state->numfree != -1);
- #endif
- if (state->numfree) {
- state->numfree--;
- op = state->free_list[state->numfree];
- _Py_NewReference((PyObject *) op);
- } else {
- // 創(chuàng)建一個(gè)新的 list
- op = PyObject_GC_New(PyListObject, &PyList_Type);
- if (op == NULL) {
- returnNULL;
- }
- }
- if (size <= 0) {
- op->ob_item = NULL;
- } else {
- op->ob_item = (PyObject **) PyMem_Calloc(size, sizeof(PyObject *));
- if (op->ob_item == NULL) {
- Py_DECREF(op);
- return PyErr_NoMemory();
- }
- }
- Py_SET_SIZE(op, size);
- op->allocated = size;
- _PyObject_GC_TRACK(op);
- return (PyObject *) op;
- }
4. list 淺拷貝
- // 源文件位置:Objects/listobject.c
- /*[clinic input]
- list.copy
- Return a shallow copy of the list.
- [clinic start generated code]*/
- // list 的 淺拷貝
- static PyObject *
- list_copy_impl(PyListObject *self)
- /*[clinic end generated code: output=ec6b72d6209d418e input=6453ab159e84771f]*/
- {
- return list_slice(self, 0, Py_SIZE(self));
- }
- // ilow、ihigh 的類型 Py_ssize_t 為當(dāng)前系統(tǒng)一個(gè)指針的大小
- static PyObject *
- list_slice(PyListObject *a, Py_ssize_t ilow, Py_ssize_t ihigh) {
- PyListObject *np;
- PyObject **src, **dest;
- Py_ssize_t i, len;
- len = ihigh - ilow;
- if (len <= 0) {
- return PyList_New(0);
- }
- // 生成新的 list
- np = (PyListObject *) list_new_prealloc(len);
- if (np == NULL)
- returnNULL;
- // 從 list 的第一個(gè)位置開(kāi)始 a->ob_item 偏移 ilow,即:移動(dòng)到 第 ilow 個(gè)數(shù)值元素的指針位置
- src = a->ob_item + ilow;
- // 新的 list 的 數(shù)值列表第一個(gè)位置
- dest = np->ob_item;
- // 進(jìn)行復(fù)制,注意:只是復(fù)制了 對(duì)象的指針
- for (i = 0; i < len; i++) {
- // src[i] 存儲(chǔ)著 指向具體的對(duì)象的指針
- PyObject *v = src[i];
- // v 的引用計(jì)數(shù) +1
- Py_INCREF(v);
- // 復(fù)制到新的list中
- // 此時(shí) 新老list底層數(shù)據(jù)對(duì)象指向相同
- dest[i] = v;
- }
- // 設(shè)置新list的size
- // ob->ob_size = size
- Py_SET_SIZE(np, len);
- return (PyObject *) np;
- }
進(jìn)行淺拷貝之后,從內(nèi)存布局發(fā)生的變化,可以看出:新、老list共享底層數(shù)據(jù)對(duì)象,這也是導(dǎo)致一個(gè)list進(jìn)行修改之后,影響其他list的原因。
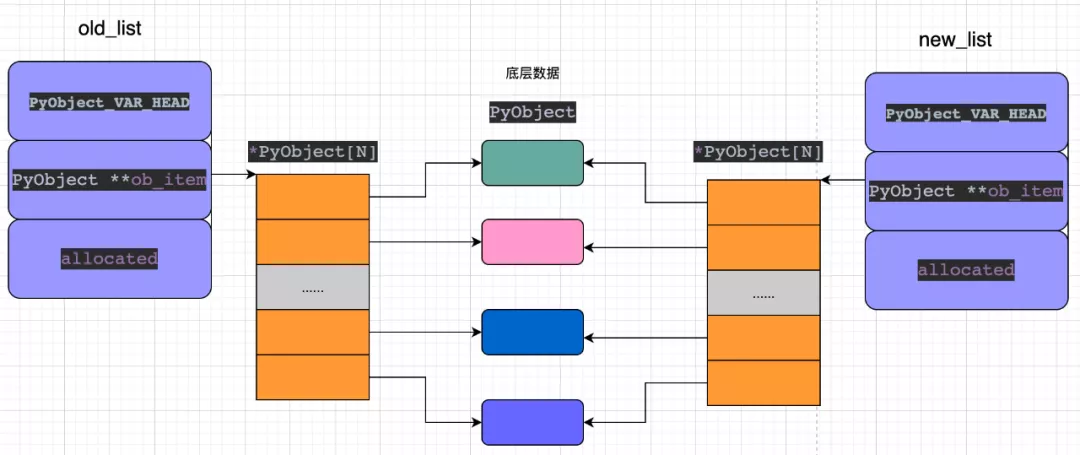
5. list 深拷貝
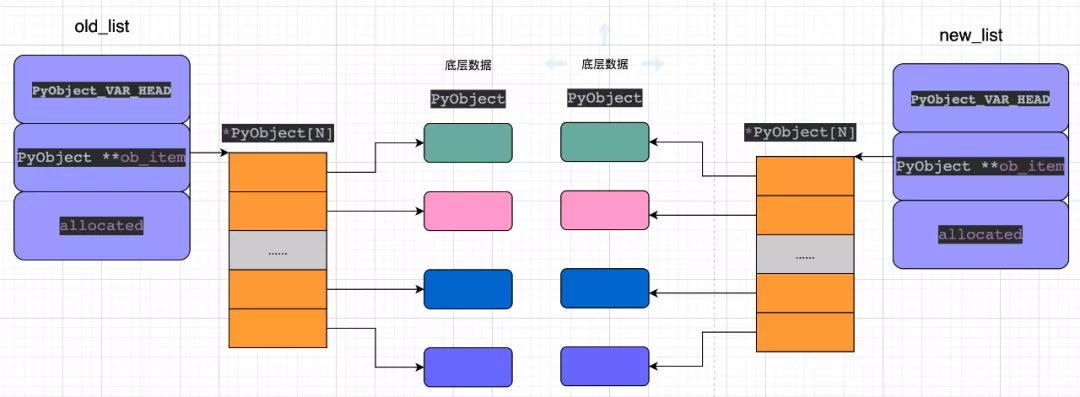
進(jìn)行深拷貝之后,從內(nèi)存布局發(fā)生的變化,可以看出:新、老list分別使用不同的底層數(shù)據(jù)對(duì)象,這就不會(huì)導(dǎo)致一個(gè)list進(jìn)行修改之后,影響其他list。
總結(jié)
通過(guò)分析python底層源碼了解到list的底層結(jié)構(gòu)以及深、淺拷貝原理,開(kāi)發(fā)過(guò)程中使用深拷貝還是淺拷貝,則需要根據(jù)實(shí)際情況來(lái)處理。
- 淺拷貝在拷貝時(shí),只拷貝第一層中的引用,如果元素是可變對(duì)象,并且被修改,那么拷貝的對(duì)象也會(huì)發(fā)生變化。
- 深拷貝在拷貝時(shí),會(huì)逐層進(jìn)行拷貝,直到所有的引用都是不可變對(duì)象為止。
- Python 有多種方式實(shí)現(xiàn)淺拷貝,copy 模塊的 copy 函數(shù) ,對(duì)象的 copy 函數(shù) ,工廠方法,切片等。
- 大多數(shù)情況下,編寫(xiě)程序時(shí),都是使用淺拷貝,除非有特定的需求。
- 淺拷貝的優(yōu)點(diǎn):拷貝速度快,占用空間少,拷貝效率高。