Go 語言的函數是“一等公民”?
1.介紹
在 Go 語言中,函數被稱為“一等公民”。實際上,在其它編程語言中,也有此說法,例如 JavaScript。
什么是編程語言的“一等公民”?Ward Cunningham 的解釋如下:
如果對如何創建和使用它沒有任何限制:當該結構可以被視為沒有限制的值時,該語言結構被稱為該語言中的 FirstClass 值。
A language construct is said to be a FirstClass value in that language when there are no restrictions on how it can be created and used: when the construct can be treated as a value without restrictions.
“一等公民”的特性是可以存儲在變量中,可以作為參數傳遞給函數,可以在函數中創建并作為返回值從函數返回。
FirstClass features can be stored in variables, passed as arguments to functions, created within functions and returned from functions. In dynamically typed languages, a FirstClass feature can also have its type examined at run-time.
本文我們介紹一下 Go 語言的函數是否符合“一等公民”的特性。
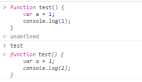
2.存儲在變量中
Go 語言的函數可以作為變量的值,存儲在變量中。
func main() {
var hello = func(name string) { fmt.Printf("hello %s\n", name) }
hello("gopher")
}閱讀上面這段代碼,我們定義一個變量 hello,和一個匿名函數,將匿名函數賦值給變量 hello,我們可以通過變量調用該匿名函數。
3.作為參數傳遞給其他函數
Go 語言的函數可以作為參數,傳遞給其他函數。
https://back-media.51cto.com/editor?id=704975/h6e90be6-6IhK9UNI
閱讀上面這段代碼,我們定義三個函數,分別是 Circle、areaOfCircle 和 perimeterOfCircle,其中 areaOfCircle 和 perimeterOfCircle 作為 Circle 的參數,分別用于計算面積和周長。
4.可以在函數中創建,并作為返回值
Go 語言的函數可以在函數體中創建,并作為返回值從函數體中返回。
func main() {
calcArea := CircleCalc("area")
fmt.Println(calcArea(5))
calcPerimeter := CircleCalc("perimeter")
fmt.Println(calcPerimeter(5))
}
func CircleCalc(s string) func(float64) float64 {
switch s {
case "area":
return func(r float64) float64 {
return math.Pi * r * r
}
case "perimeter":
return func(r float64) float64 {
return 2 * math.Pi * r
}
default:
return nil
}
}閱讀上面這段代碼,我們定義一個函數 CircleCalc,在其函數體中定義兩個匿名函數,并將匿名函數作為返回值從函數體中返回。
5.總結
本文我們通過三段示例代碼,證明 Go 語言中函數符合“一等公民”的特性,我們可以使用這些特性,使業務代碼更加簡潔。