Linux高性能編程-時間輪
大家好,這里是物聯網心球。
本期我們來聊聊時間輪,話不多說我們直接開始今天的主題。
1.初識時間輪
時間輪(TimingWheel)是一個環形隊列,底層采用數組實現,數組中每個元素都是一個鏈表,鏈表中存儲的是一個個定時任務。
定時任務可以分為:延時任務,周期性任務。
時間輪是一種非常重要的機制,通過時間輪可以輕松實現各種功能:
- 心跳機制。
- 周期性獲取系統狀態。
- 計時功能。
- 通知功能。
- ......
很多著名的開源軟件都使用了時間輪,如:kafka,skynet,Linux內核等。
所以實現一個高效的時間輪對于我們的軟件非常重要。
2.時間輪實現原理
2.1 時間輪整體架構
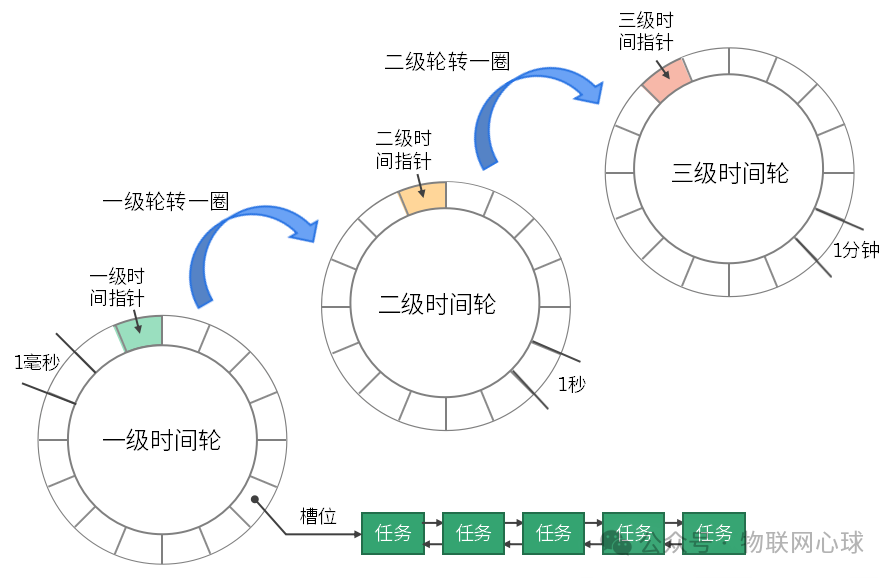 圖片
圖片
時間輪主要由:時間輪盤,時間指針,定時任務,時間驅動器四部分組成。
1)時間輪盤
時間輪盤由固定數量槽位(wheelSize)構成,每個槽位對應一個時間跨度(tickMS),wheelSize*tickMS為時間輪最大時間跨度,定時任務的最大定時時間不能超過最高級時間輪的最大時間跨度。
定時任務的最小定時時間不能低于最低級時間輪的tickMS。
時間指針會記錄時間輪的槽位位置,當時間指針指向一個槽位時,表示該槽位的任務鏈表中的任務需要被處理,如果當前時間到達任務的到期時間(expire time)則執行任務的回調函數,否則任務被重映射到上一級時間輪對應槽位。
2)時間指針
時間指針記錄當前層級時間輪槽位位置,每一級時間輪的時間跨度不一樣,各個層級的時間輪時間指針會存在一定的倍數關系(由用戶自定義),低級時間輪時間指針轉一周之后,上一級時間輪才會移動一個槽位。
3)定時任務
時間輪可以處理大批量定時任務,定時任務以鏈表的形式存儲在每一個槽位,每個任務都由用戶自定義功能,且每個任務都有到期時間和周期時間記錄。
4)時間驅動器
時間驅動器就像電池一樣,推動時間輪的運轉,相當于一個定時刷新的功能模塊。時間驅動器通常由一個單獨的線程通過sleep或者其他超時機制實現。
2.2 從0到1實現一個時間輪
要實現一個高效的時間輪,我們得結合具體的業務確定:
- 每級時間輪時間跨度和大小
- 時間輪的層級數。
- 時間輪驅動器類型。
接著我們就可以完成時間輪盤,時間指針,定時任務,時間驅動器的設計。
本示例:
一級時間輪:時間跨度1秒,時間輪大小256。
二級時間輪:時間跨度256 * 1秒,時間輪大小256。
二級時間輪:時間跨度256 * 256 * 1秒,時間輪大小256。
時間驅動器:sleep和epoll可選。
2.2.1 組件設計
1)時間輪盤設計
struct tw {
uint32_t tick_ms;
uint32_t cur_tick;
struct link slots[TW_LEVEL][TW_SIZE];
pthread_spinlock_t lock;
};時間輪盤定義了四個成員:
- tick_ms:時間精度,最低級時間輪時間跨度。
- cur_tick:當前時間,通過當前時間計算當前時間指針,確定定時任務所在槽位。
- slots:槽位,用于存儲定時任務,定時任務以單鏈表形式存儲。TW_LEVEL:時間輪層級數。
TW_SIZE:時間輪大小(槽位數量)。
- lock:自旋鎖,保證多線程對任務鏈表的安全操作。
2)時間指針設計
時間指針按照時間輪的層級可以分為:一級時間指針,二級時間指針,三級時間指針,......。
代碼設計并不一定要為每個時間指針定義一個變量,我們定義一個總的時間指針,總的時間指針通過位運算的獲取每一級時間指針。
#define TW_BITS (8)
#define TW_SIZE (1 << TW_BITS) //單級時間輪大小(槽位數量)
#define TW_MASK (TW_SIZE - 1)
#define IDX0(data) data & TW_MASK; //獲取一級指針
#define IDX1(data) (data >> TW_BITS) & TW_MASK; //獲取二級指針
#define IDX2(data) (data >> (2 * TW_BITS)) & TW_MASK;//獲取三級指針通過時間指針就能準確定位到時間輪盤上的槽位,找到對應的定時任務。
3)定時任務設計
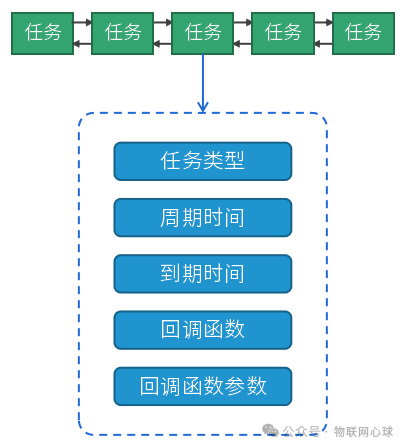 圖片
圖片
一個完整的定時任務,需要具備:任務類型,周期時間,到期時間,回調函數,回調函數參數等成員。
這樣才能完成一次性任務,周期性任務,自定義任務等功能。
typedef void (*func)(void *arg);
struct tw_node {
struct link link;
int32_t expire_tick;
int32_t period_ticks;
int flags;
func cb;
void *arg;
};- link:單向鏈表節點,用于任務插入和移除操作。
- expire_tick:定時任務到期時間,定時任務根據到期時間插入指定的槽位,并且更新時間輪時,根據到期時間決定任務是否被執行或者重映射。
- period_ticks:周期性任務周期時間。
- flags:任務類型,分為:一次性任務和周期性任務。
#define ONESHOT_FLAG 0x1 //一次性任務,只執行一次
#define PERIOD_FLAG 0x2 //周期性任務,周期性執行
- cb:定時任務回調函數。
- arg:定時任務回調函數參數。
4)時間驅動器設計
時間輪運轉通過時間驅動器驅動,時間驅動器是周期性更新時間輪的機制。目前用的比較多的方法:sleep和epoll方法。
方法1:sleep方式
void *tw_driver_thread(void *arg) {
struct tw *tw = (struct tw *)arg;
while(1) {
usleep(TICK_MS * 1000);
tw_update(tw);
}
}sleep方法設計比較簡單,while循環每一次循環調用usleep休眠指定的時間間隔(時間精度),休眠結束后更新時間輪指針。
方法二:epoll方式
void *tw_driver_thread(void *arg) {
struct tw *tw = (struct tw *)arg;
int efd = epoll_create(1024);
if (efd == -1) {
perror("epoll create error");
return NULL;
}
struct epoll_event ev, events[MAX_EVENTS];
while(1) {
int nfds = epoll_wait(efd, events, MAX_EVENTS, TICK_MS);
if (nfds == -1) {
perror("epoll wait error");
break;
}
tw_update(tw);
}
}epoll方式設計相對來說比較復雜,該方式借用epoll_wait超時機制實現精確定時,epoll方式除了定時之外,還可以借用epoll實現網絡IO檢測功能。
2.2.2 接口設計
時間輪重要接口定義:
// 1.初始化時間輪
void tw_init(struct tw *tw, uint32_t tick_ms);
// 2.釋放時間輪
void tw_free(struct tw *tw);
// 3.添加定時任務
void tw_add(struct tw *tw, struct tw_node *node, bool
nolock);
// 4.驅動時間輪
int tw_update(struct tw *tw);其中tw_add和tw_update函數是難點和重點。
1)tw_add添加定時任務
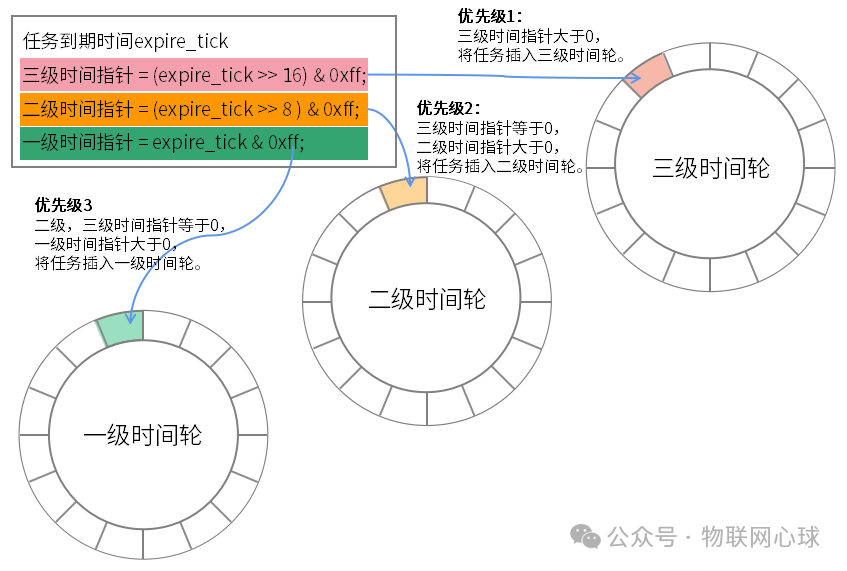 圖片
圖片
定時任務添加至時間輪首次到期時間=時間輪當前時間+任務延遲時間。
通過到期時間可以計算出每級時間輪的時間指針,定時任務插入優先級:三級時間輪>二級時間輪>一級時間輪。
周期性任務執行完后,需根據任務周期時間和當前時間重新計算到期時間,并根據到期時間再次將任務插入時間輪。
2)tw_update驅動時間輪
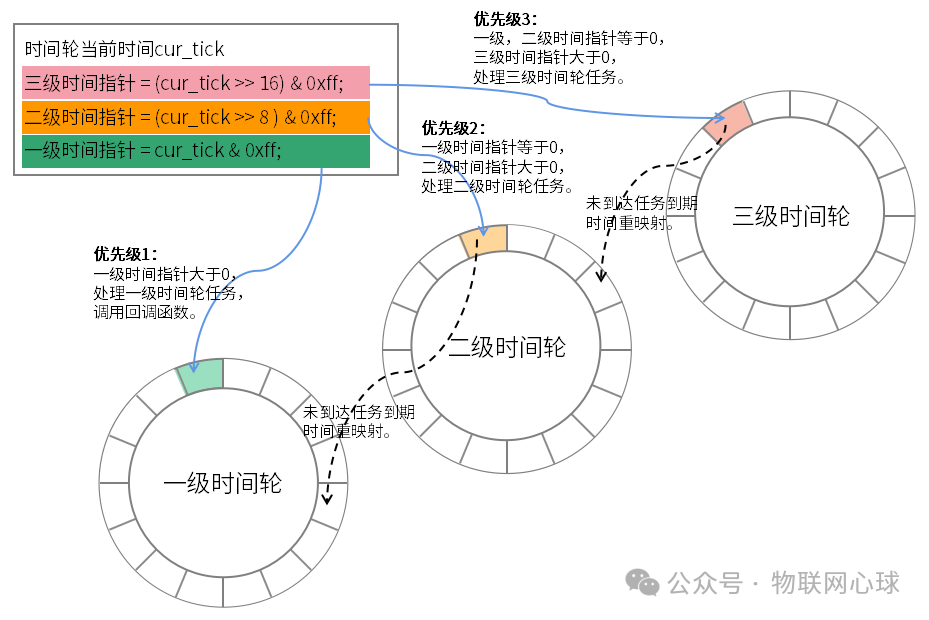 圖片
圖片
時間驅動器后定時調用tw_update函數,tw_update每調用一次,時間輪的當前時間會增加1,根據當前時間獲取到一級,二級,三級時間指針。
如果一級時間指針大于0,說明此時一級時間輪還沒轉夠一周,該情況只需要處理一級時間指針指向的定時任務。
如果一級時間指針等于0,二級時間指針大于0,說明一級時間輪已經轉了一周,此時處理二級時間指針指向定時任務。如果定時任務的過期時間和當前時間相等,則直接調用定時任務回調函數,如果不相等則將定時任務重新插入過期時間一級時間指針指向的槽位。
如果一級,二級時間指針都等于0,三級時間指針大于0,說明一級,二級時間輪都轉了一周,此時需要處理三級時間指針指向的定時任務。如果定時任務的過期時間和當前時間相等,則直接調用定時任務回調函數,如果不相等則將定時任務重新插入過期時間二級時間指針指向的槽位。
3.時間輪測試
3.1 測試代碼
測試代碼是一份完整的時間輪代碼,可以直接編譯測試。
時間精度1秒,時間輪大小256,采用三級時間輪。
定時任務為英雄聯盟劍圣技能冷卻,每個技能都是一個延時任務:
- Q技能:冷卻時間14秒,持續時間1秒。
- W技能:冷卻時間35秒,持續時間5秒。
- E技能:冷卻時間14秒,持續時間5秒。
- R技能:冷卻時間75秒,持續時間10秒。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <sys/epoll.h>
#define TW_BITS (8)
#define TW_SIZE (1 << TW_BITS) //單級時間輪大小(槽位數量)
#define TW_MASK (TW_SIZE - 1)
#define TW_LEVEL (3) //時間輪層級數
#define IDX0(data) data & TW_MASK;
#define IDX1(data) (data >> TW_BITS) & TW_MASK;
#define IDX2(data) (data >> (2 * TW_BITS)) & TW_MASK;
#define ONESHOT_FLAG 0x1 //一次性任務
#define PERIOD_FLAG 0x2 //周期性任務
#define TICK_MS (1000) //單次延時時間,單位毫秒
#define MS_TO_TICKS(ms, tick_ms) (ms/tick_ms)
#define TW_DRIVER_TYPE (1) //時間驅動器類型
#define SLEEP_DRIVER (0) //sleep時間驅動器
#define EPOLL_DRIVER (1) //epoll時間驅動器
#define MAX_EVENTS (10)
struct link {
struct link *next;
};
void link_init(struct link *link) {
link->next = NULL;
}
void link_add(struct link *link, struct link *it) {
it->next = link->next;
link->next = it;
}
struct link *link_del(struct link *link) {
if (!link->next) return NULL;
struct link *it = link->next;
link->next = it->next;
return it;
}
typedef void (*func)(void *arg);
struct tw_node {
struct link link;
int32_t expire_tick;
int32_t period_ticks;
int flags;
func cb;
void *arg;
bool need_free;
};
struct tw {
uint32_t tick_ms;
uint32_t cur_tick;
struct link slots[TW_LEVEL][TW_SIZE];
pthread_spinlock_t lock;
};
struct tw_node *tw_node_new(struct tw *tw, int expire_ms, int period_ms, int flags, func cb, void *arg, bool need_free) {
if ((expire_ms < TICK_MS) || (period_ms < TICK_MS)) {
return NULL;
}
struct tw_node *node = (struct tw_node*)malloc(sizeof(struct tw_node));
if (!node) return NULL;
memset(node, 0, sizeof(struct tw_node));
node->expire_tick = MS_TO_TICKS(expire_ms, tw->tick_ms);
node->period_ticks = MS_TO_TICKS(period_ms, tw->tick_ms);
//printf("tw node new expire tick:%u,%u, peroid ticks:%u,%u\n", expire_ms, node->expire_tick, period_ms, node->period_ticks);
node->flags = flags;
node->cb = cb;
node->arg = arg;
node->need_free = need_free;
return node;
}
void tw_node_free(struct tw_node *node) {
if (node->arg && node->need_free) {
uint32_t *task_id = (uint32_t *)node->arg;
printf("free task id:%u node\n", *task_id);
free(node->arg);
}
free(node);
}
void tw_init(struct tw *tw, uint32_t tick_ms) {
memset(tw, 0, sizeof(struct tw));
tw->tick_ms = tick_ms;
pthread_spin_init(&tw->lock, PTHREAD_PROCESS_PRIVATE);
}
void tw_free(struct tw *tw) {
pthread_spin_lock(&tw->lock);
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < TW_LEVEL; i++) {
for (uint32_t j = 0; j < TW_SIZE; j++) {
struct link *link = &tw->slots[i][j];
struct link *it;
while(it = link_del(link)) {
printf("free i:%u, j:%u\n", i, j);
struct tw_node *node = (struct tw_node *)it;
tw_node_free(node);
}
}
}
pthread_spin_unlock(&tw->lock);
pthread_spin_destroy(&tw->lock);
}
void tw_add(struct tw *tw, struct tw_node *node, bool nolock) {
if (!nolock) pthread_spin_lock(&tw->lock);
uint32_t expire_tick = node->expire_tick;
node->expire_tick += tw->cur_tick;
#if 0
printf("tw add cur tick:%u, period ticks:%u, old expire tick:%u, node expire tick:%u\n",
tw->cur_tick,
node->period_ticks,
expire_tick,
node->expire_tick);
#endif
uint8_t idx0 = IDX0(tw->cur_tick);
uint8_t idx1 = IDX1(tw->cur_tick);
uint8_t idx2 = IDX2(tw->cur_tick);
uint8_t e0 = IDX0(node->expire_tick);
uint8_t e1 = IDX1(node->expire_tick);
uint8_t e2 = IDX2(node->expire_tick);
//printf("tw add e0,e1,e2:%u,%u,%u\n", e0, e1, e2);
struct link *it = &node->link;
if (e2 != idx2) {
struct link *link = &tw->slots[2][e2];
//printf("tw link add 2,e2:%u\n", e2);
link_add(link, it);
} else if (e1 != idx1) {
struct link *link = &tw->slots[1][e1];
//printf("tw link add 1,e1:%u\n", e1);
link_add(link, it);
} else if (e0 != idx0){
struct link *link = &tw->slots[0][e0];
//printf("tw link add 0,e0:%u\n", e0);
link_add(link, it);
}
if (!nolock) pthread_spin_unlock(&tw->lock);
}
int tw_update(struct tw *tw) {
pthread_spin_lock(&tw->lock);
tw->cur_tick++;
uint8_t idx0 = IDX0(tw->cur_tick);
uint8_t idx1 = IDX1(tw->cur_tick);
uint8_t idx2 = IDX2(tw->cur_tick);
struct link active = {0};
if ((idx0 == 0) && (idx1 == 0) && (idx2 > 0)) {
struct link *link = &tw->slots[2][idx2];
struct link *it;
while(it = link_del(link)) {
//printf("tw update cur tick:%u, idx0:%u,idx1:%u,idx2:%u\n", tw->cur_tick, idx0, idx1, idx2);
struct tw_node *node = (struct tw_node *)it;
uint8_t e0 = IDX0(node->expire_tick);
uint8_t e1 = IDX1(node->expire_tick);
if ((e0 == 0) && (e1 == 0)) {
link_add(&active, it);
} else if (e1 > 0) {
struct link *l = &tw->slots[1][e1];
link_add(l, it);
} else {
struct link *l = &tw->slots[0][e0];
link_add(l, it);
}
}
} else if ((idx0 == 0) && (idx1 > 0)) {
struct link *link = &tw->slots[1][idx1];
struct link *it;
while(it = link_del(link)) {
//printf("tw update cur tick:%u, idx0:%u,idx1:%u,idx2:%u\n", tw->cur_tick, idx0, idx1, idx2);
struct tw_node *node = (struct tw_node *)it;
uint8_t e0 = IDX0(node->expire_tick);
if (e0 == 0) {
link_add(&active, it);
} else {
struct link *l = &tw->slots[0][e0];
link_add(l, it);
}
}
} else if (idx0 > 0) {
struct link *link = &tw->slots[0][idx0];
struct link *it;
while(it = link_del(link)) {
//printf("tw update cur tick:%u, idx0:%u,idx1:%u,idx2:%u\n", tw->cur_tick, idx0, idx1, idx2);
link_add(&active, it);
}
}
struct link *it;
while(it = link_del(&active)) {
struct tw_node *node = (struct tw_node *)it;
//printf("tw update callback cur tick:%u@@\n", tw->cur_tick);
node->cb(node->arg);
if (node->flags & PERIOD_FLAG) {
node->expire_tick = node->period_ticks;
tw_add(tw, node, true);
} else {
tw_node_free(node);
}
}
pthread_spin_unlock(&tw->lock);
return 0;
}
void get_time(char *buffer) {
struct timeval tv;
gettimeofday(&tv, NULL);
strftime(buffer, 40, "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", localtime(&tv.tv_sec));
sprintf(buffer + strlen(buffer), ".%03ld", tv.tv_usec / 1000);
}
void *tw_driver_thread(void *arg) {
struct tw *tw = (struct tw *)arg;
#if (TW_DRIVER_TYPE == EPOLL_DRIVER)
int efd = epoll_create(1024);
if (efd == -1) {
perror("epoll create error");
return NULL;
}
struct epoll_event ev, events[MAX_EVENTS];
#endif
while(1) {
#if (TW_DRIVER_TYPE == SLEEP_DRIVER)
usleep(TICK_MS * 1000);
tw_update(tw);
//printf("sleep driver\n");
#else
int nfds = epoll_wait(efd, events, MAX_EVENTS, TICK_MS);
if (nfds == -1) {
perror("epoll wait error");
break;
}
//printf("epoll driver nfds:%d\n", nfds);
tw_update(tw);
#endif
}
}
struct skill {
char skill_name[20];
char ch;
int cool_time;
int duration_time;
bool ready;
};
struct hero {
char hero_name[20];
struct skill Q;
struct skill W;
struct skill E;
struct skill R;
};
void skill_task(void *arg) {
struct skill *sk = (struct skill *)arg;
sk->ready = true;
char buf[40] = {0};
get_time(buf);
printf("%s %s 完成冷卻!\n", buf, sk->skill_name);
}
void *task_scheduler_thread(void *arg) {
struct tw *tw = (struct tw *)arg;
struct hero yi = (struct hero) {
.hero_name = "易大師",
.Q = {.skill_name = "Q技能", .ch = 'q', .cool_time = 14, .duration_time = 1, .ready = true},
.W = {.skill_name = "W技能", .ch = 'w', .cool_time = 35, .duration_time = 5, .ready = true},
.E = {.skill_name = "E技能", .ch = 'e', .cool_time = 14, .duration_time = 5, .ready = true},
.R = {.skill_name = "R技能", .ch = 'r', .cool_time = 75, .duration_time = 10, .ready = true},
};
while(1) {
int ch = getchar();
if (ch == '\n') continue;
switch (ch) {
case 'q':
if (yi.Q.ready == false) {
printf("%s %s 冷卻中......\n", yi.hero_name, yi.Q.skill_name);
} else {
char buf[40] = {0};
get_time(buf);
printf("%s %s 施放 %s QQQQQQQQQQQQQQQ\n", buf, yi.hero_name, yi.Q.skill_name);
yi.Q.ready = false;
struct tw_node *node = tw_node_new(tw, yi.Q.cool_time * 1000, 1000, ONESHOT_FLAG, skill_task, (void *)&yi.Q, false);
if (!node) {
printf("tw node new error\n");
break;
}
tw_add(tw, node, false);
}
break;
case 'w':
if (yi.W.ready == false) {
printf("%s %s 冷卻中......\n", yi.hero_name, yi.W.skill_name);
} else {
char buf[40] = {0};
get_time(buf);
printf("%s %s 施放 %s WWWWWWWWWWWWWW\n", buf, yi.hero_name, yi.W.skill_name);
yi.W.ready = false;
struct tw_node *node = tw_node_new(tw, yi.W.cool_time * 1000, 1000, ONESHOT_FLAG, skill_task, (void *)&yi.W, false);
if (!node) {
printf("tw node new error\n");
break;
}
tw_add(tw, node, false);
}
break;
case 'e':
if (yi.E.ready == false) {
printf("%s %s 冷卻中......\n", yi.hero_name, yi.E.skill_name);
} else {
char buf[40] = {0};
get_time(buf);
yi.E.ready = false;
printf("%s %s 施放 %s EEEEEEEEEEEEEE\n", buf, yi.hero_name, yi.E.skill_name);
struct tw_node *node = tw_node_new(tw, yi.E.cool_time * 1000, 1000, ONESHOT_FLAG, skill_task, (void *)&yi.E, false);
if (!node) {
printf("tw node new error\n");
break;
}
tw_add(tw, node, false);
}
break;
case 'r':
if (yi.R.ready == false) {
printf("%s %s 冷卻中......\n", yi.hero_name, yi.R.skill_name);
} else {
char buf[40] = {0};
get_time(buf);
printf("%s %s 施放 %s RRRRRRRRRRRRRRR\n", buf, yi.hero_name, yi.R.skill_name);
yi.R.ready = false;
struct tw_node *node = tw_node_new(tw, yi.R.cool_time * 1000, 1000, ONESHOT_FLAG, skill_task, (void *)&yi.R, false);
if (!node) {
printf("tw node new error\n");
break;
}
tw_add(tw, node, false);
}
break;
default:
printf("xxx無效技能:%c\n", ch);
break;
}
}
return NULL;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
struct tw tw;
tw_init(&tw, TICK_MS);
pthread_t th1;
pthread_create(&th1, NULL, task_scheduler_thread, (void *)&tw);
pthread_t th2;
pthread_create(&th2, NULL, tw_driver_thread, (void *)&tw);
pthread_join(th1, NULL);
pthread_join(th2, NULL);
printf("start free timewheel\n");
tw_free(&tw);
return 0;
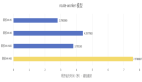
}3.2 測試結果
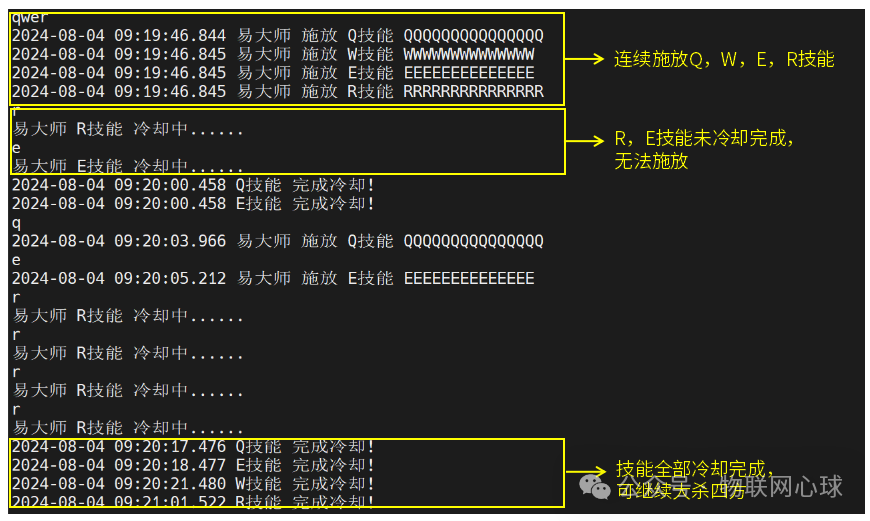 圖片
圖片
總結:
時間輪可以處理大批量延時任務和周期性任務,是非常實用的一個軟件模塊,小伙伴可以自己動手實現一個時間輪。